Foot Drop
Overview
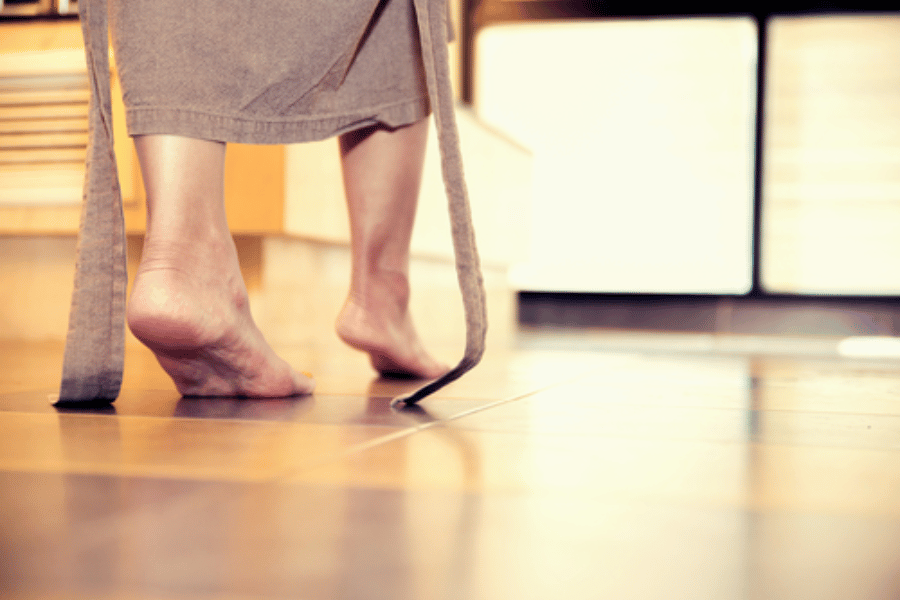

Foot drop is a condition where the forefoot cannot be lifted due to weakness in the dorsiflexion of the foot.
This can result in an unsafe gait, increasing the risk of falls.
The causes of foot drop can be muscular, neurologic, spinal, autoimmune, or musculoskeletal, and the treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause.
Understanding the pathophysiology is essential to devise an appropriate treatment plan. This article will delve into the etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of foot drop.
By exploring these aspects, individuals with foot drop and healthcare professionals can better understand this condition and how best to manage it.
Symptoms
• Foot drop hampers lift the front foot, leading to dragging while walking.
• Symptoms include foot or toe lifting challenges and a steppage gait.
• Slapping the foot down while walking and numbness in the foot are common.
• Weakness in ankle muscles and loss of control over foot movement occur.
• Individuals may experience tingling sensations and difficulty balancing.
• These symptoms can significantly impact mobility and daily activities.
Causes & Risks
• Foot drop is characterized by difficulty lifting the front part of the foot, leading to dragging while walking.
• It can result from various factors, including nerve injuries, muscle or nerve disorders, and brain and spinal cord disorders.
• Nerve injuries may occur due to severe knee injuries, hip or knee replacement surgeries, or a "pinched nerve" in the spine.
• Muscle or nerve disorders can be caused by inherited diseases like muscular dystrophy or neurologic disorders like polio or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
• Brain and spinal cord disorders, such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, or ALS, can also contribute to foot drop.
• Certain habits like leg crossing, prolonged kneeling, and wearing a leg cast can increase the risk of developing foot drop.
Test & Diagnosis
• Foot drop is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, where a healthcare provider evaluates your gait and muscle strength, focusing on leg weakness.
• Sensation in the shin, top of the foot, and toes may also be assessed to gauge numbness.
• Conditions like bone overgrowth in the spinal canal or nerve-pressing masses, such as cysts or tumors, can lead to foot drop.
• Imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs are commonly used to detect underlying issues.
• These tests are crucial for identifying bone abnormalities and soft tissue lesions responsible for the symptoms.
• Early detection through imaging helps in prompt treatment and management of foot drop-related conditions.
Treatment
• Treatment for foot drop varies based on its cause; addressing the root issue can lead to improvement or resolution.
• Braces or splints may be worn to maintain foot position, while shoe splints can aid in normalizing foot posture.
• Physical therapy exercises are crucial for strengthening leg muscles and addressing gait abnormalities.
• Nerve stimulation techniques can be used to assist in foot elevation.
• Nerve surgery may be beneficial for recent cases of foot drop, while long-standing conditions may require tendon transfer surgery.
• Surgical interventions aim to restore foot function by transferring a functional tendon to affected areas.
Living With
Living with foot drop can pose challenges, but a collaborative approach involving healthcare providers, physical therapists, and orthotists can enhance mobility and symptom management.
Customized treatments, including assistive devices like braces and splints, aid in gait improvement and fall prevention.
Adaptive strategies and assistive technology further enhance daily activities and quality of life.
Regular exercise and physical therapy boost strength, flexibility, and injury prevention.
With comprehensive support, individuals with foot drop can maintain independence and lead fulfilling lives, despite the condition's challenges.
It's crucial for individuals with foot drop to seek assistance from a multidisciplinary team and explore various treatment options to optimize their functional abilities and overall well-being.
Complications
1. Foot drop is a symptom, not a disease, stemming from issues in muscles, nerves, or the nervous system.
2. It poses challenges like difficulty walking due to an inability to lift the front of the foot, increasing the risk of falls.
3. Complications include reduced mobility, muscle weakness, joint pain, and psychosocial impacts.
4. Improper footwear or dragging the foot can cause skin irritation, blisters, or pressure sores.
5. Coping with foot drop limitations may lead to emotional stress, frustration, or social isolation.
6. Addressing these complications requires a comprehensive approach involving medical care and lifestyle adjustments.

The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Know more about
Our Healthcare Planner
Personal Health Planner at BNC is a support staff who listens to your concerns and connects you with a Neuro Care provider. They prioritize your needs and create a trusting relationship between you and the provider.
Three fundamental values we can assure you:
1. Personalized Healthcare.
2. Most advanced robotic therapies
3. Transparent pricing